Indonesia is developing a new Tuberculosis (TB) vaccine to strengthen the fight against TB, which has claimed an average of 150,000 lives annually.
Indonesia’s Accelerated Efforts in TB Vaccine Development
Introduction
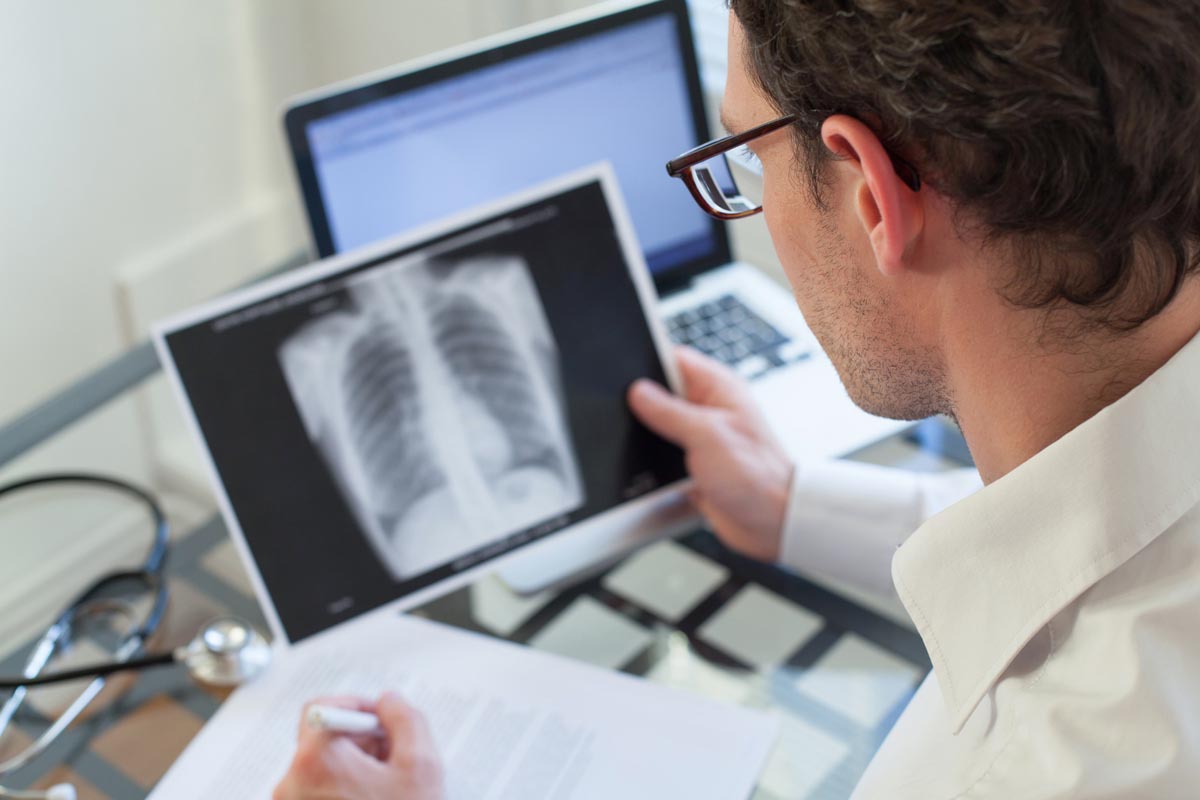
Tuberculosis remains a major global health challenge, particularly in Indonesia, where the disease burden is substantial. As one of the top five countries with the highest incidence of , Indonesia is intensifying its efforts to develop a new vaccine to combat the rising cases. This essay explores Indonesia’s accelerated approach to vaccine development, examining the current situation, the challenges faced, the progress made in vaccine research, and the implications for public health.
Table of Contents
The Current TB Situation in Indonesia
Indonesia ranks among the world’s highest iincidence and mortality rates. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the country reported approximately 842,000 new cases in 2020, contributing to a significant portion of the global burden. The disease’s persistence in Indonesia is attributed to factors such as high population density, inadequate healthcare infrastructure, and socio-economic determinants like poverty and poor living conditions.
indianfastearning.comhttps://indianfastearning.com/
The disease spreads through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes, making it highly transmissible. Despite efforts to control through existing measures, including the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine and directly observed treatment short-course (DOTS), the incidence of remains high in Indonesia.
youtube.comhttps://youtu.be/maGG1xEqCwc?si=ceaL4tWEadDZa5IH
Challenges in TB Control
Several challenges complicate control efforts in Indonesia. First, the current BCG vaccine, introduced in the 1920s, provides limited protection against adult pulmonary the most common form of the disease. It is more effective in preventing severe forms of in children but less so in adults, who are the primary transmitters of the disease.
Second, the rise of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) strains poses a significant threat. MDR- and XDR- are resistant to standard treatments, making them more difficult and expensive to treat. These strains have emerged due to incomplete or improper treatment regimens, highlighting the need for more effective vaccines and treatments.
Third, logistical and financial constraints hinder control efforts. Inadequate funding, insufficient healthcare infrastructure, and a shortage of trained healthcare professionals impede the effective implementation of control programs. The need for more robust and sustainable approaches to management is evident.
Progress in Vaccine Research
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, Indonesia has ramped up efforts to accelerate vaccine development. The development of a new vaccine is crucial for enhancing disease prevention and control. Several strategies and advancements have been pursued to achieve this goal:
- Collaborative Research Initiatives: Indonesia has fostered partnerships with international organizations, research institutions, and pharmaceutical companies to advance vaccine research. Collaborative efforts help pool resources, expertise, and technology, accelerating the development process. Notable partnerships include collaborations with organizations like the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the World Health Organization.
- Innovative Vaccine Candidates: Researchers are exploring various innovative vaccine candidates to address the limitations of the BCG vaccine. For instance, new vaccines are being developed to target both latent and active with an emphasis on enhancing immune responses and providing broader protection. Promising candidates include subunit vaccines, viral vector vaccines, and recombinant protein vaccines.
- Clinical Trials and Testing: Clinical trials are a crucial phase in vaccine development. Indonesia has been actively involved in conducting clinical trials for new vaccine candidates. These trials assess the safety and efficacy of the vaccines in different populations and settings. Successful trials are essential for regulatory approval and eventual widespread use of the vaccine.
- Strengthening Research Capacity: Enhancing research capacity and infrastructure is vital for advancing vaccine development. Indonesia has invested in strengthening its research facilities, training researchers, and improving laboratory capabilities. These investments contribute to the country’s ability to conduct high-quality research and development activities.
Implications for Public Health
The successful development and deployment of a new vaccine have significant implications for public health in Indonesia. A more effective vaccine could:
- Reduce TB Incidence and Mortality: A new vaccine with improved efficacy could significantly reduce the incidence and mortality of TB. By preventing new infections and reducing transmission rates, the vaccine would contribute to overall disease control and alleviate the burden on the healthcare system.
- Address Drug Resistance: An effective vaccine could help mitigate the spread of drug-resistant TB strains. By preventing primary infections, the vaccine would reduce the number of individuals requiring treatment, thereby decreasing the risk of developing drug resistance.
- Improve Health Outcomes: Enhanced vaccination coverage and protection could lead to better health outcomes for individuals and communities. Reduced TB incidence would improve the quality of life and productivity of affected populations.
- Economic Impact: The economic burden of TB is substantial, including healthcare costs, lost productivity, and socioeconomic impacts. A new vaccine could lead to cost savings by reducing the need for extensive treatment and minimizing the economic impact of the disease.
Conclusion
Indonesia’s accelerated efforts in TB vaccine development represent a critical response to the growing TB burden. By addressing the limitations of the current BCG vaccine, tackling drug resistance, and strengthening research capacities, Indonesia aims to make significant strides in TB control. The successful development and implementation of a new TB vaccine have the potential to transform public health outcomes, reduce TB incidence and mortality, and alleviate the economic and social impacts of the disease. Continued investment, collaboration, and innovation will be key to achieving these goals and ultimately improving the health and well-being of the Indonesian population.







